Morse code
From Wikipedia
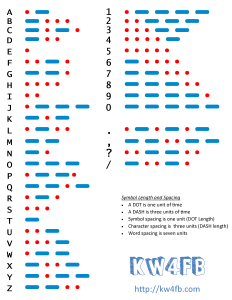
Chart of the Morse code 26 letters and 10 numerals.[1]
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal duration, called dots and dashes or dits and dahs. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, an inventor of the telegraph.
International Morse Code, also known as Continental Morse Code, encodes the 26 English letters A through Z, some non-English letters, the Arabic numerals and a small set of punctuation and procedural signals (prosigns). There is no distinction between upper and lower case letters. Each Morse code symbol is formed by a sequence of dots and dashes. The dot duration is the basic unit of time measurement in Morse code transmission. The duration of a dash is three times the duration of a dot. Each dot or dash within a character is followed by period of signal absence, called a space, equal to the dot duration. The letters of a word are separated by a space of duration equal to three dots, and the words are separated by a space equal to seven dots.[1] To increase the efficiency of encoding, Morse code was designed so that the length of each symbol is approximately inverse to the frequency of occurrence of the character that it represents in text of the English language. Thus the most common letter in English, the letter "E", has the shortest code: a single dot. Because the Morse code elements are specified by proportion rather than specific time duration, the code is usually transmitted at the highest rate that the receiver is capable of decoding. The Morse code transmission rate (speed) is specified in groups per minute, commonly referred to as words per minute.[5]
Morse code is usually transmitted by on-off keying of an information-carrying medium such as electric current, radio waves, visible light, or sound waves. The current or wave is present during the time period of the dot or dash and absent during the time between dots and dashes.
Morse code can be memorized, and Morse code signalling in a form perceptible to the human senses, such as sound waves or visible light, can be directly interpreted by persons trained in the skill.
Because many non-English natural languages use other than the 26 Roman letters, Morse alphabets have been developed for those languages.

SOS, the standard emergency signal, is a Morse code Prosign
In an emergency, Morse code can be generated by improvised methods such as turning a light on and off, tapping on an object or sounding a horn or whistle, making it one of the simplest and most versatile methods of telecommunication. The most common distress signal is SOS – three dots, three dashes, and three dots – internationally recognized by treaty.
Glossary - See Glossary for terms used on the show.
Thanks KW4FB for the graphic
Contact Info For Richard KB5JBV: Website: www.rfpodcast.info Email: kb5jbv@gmail.com Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/c/RichardBaileyKB5JBV FaceBook: www.facebook.com/groups/resonantfrequency/ Twitter: www.twitter.com/kb5jbv MeWE: mewe.com/i/richardbailey31 Tumblr https://www.tumblr.com/settings/blog/resonant-frequency-podcast Discord: https://discord.com/channels/758866379104845856/758866379104845860 Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/user/Richard_KB5JBV
